Syzygium jambos (L.) Alston
ചാമ്പ
Family : Myrtaceae
Synonym : Jambosa vulgaris
DC.
Common Names : Sheemachampa, Champa, Malaykachampa, Malabar plum
Flowering Period : October-January
Distribution : Native of Malaysia, planted in tropical Asia and Australia
Habitat : Cultivated
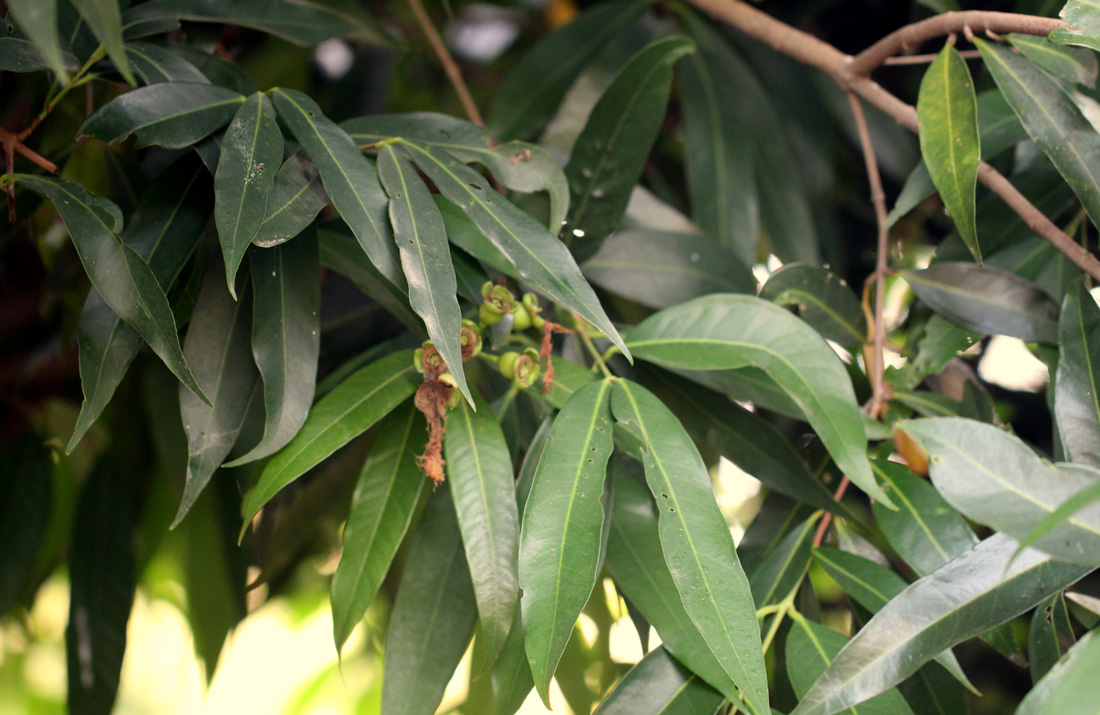

Uses : Fruit - usually eaten raw, the fruit can also be stewed, made into jams, jellies, confections etc. The fruit can be distilled to yield a rosewater that is said to be equal to the best obtained from rose petals. In India, the fruit is regarded as a tonic for the brain and liver. An infusion of the fruit acts as a diuretic. The seeds are employed against diarrhoea, dysentery. The leaf decoction is applied to sore eyes, also serves as a diuretic and expectorant and treatment for rheumatism. The bark contains 7-12.4% tannin. It is astringent, emetic and cathartic. A yellow coloured essential oil, important in the perfume industry, is derived from the leaves by distillation. The heartwood is dark-red or brown; the sapwood is white. The wood is straight and close-grained, medium-heavy to heavy, strong. It is not durable in the ground and is prone to attack by dry wood termites.
Key Characters : Trees,
to 15 m high. Leaves simple, opposite, decussate; lamina elliptic,
elliptic-oblong. Flowers bisexual, white, terminal cymes; calyx tube,
persistent; petals 4; stamens many; ovary inferior, 2-celled, ovules many.
Fruit a berry, white or pink, fleshy, oblong; seeds brown.


 Home
Home