Senna siamea
(Lam.) Irwin & Barneby
മഞ്ഞക്കൊന്ന
Family : Leguminosae (Caesalpinioideae)
Synonym : Cassia siamea Lam., Cassia florida Vahl
Common Names : Manjakonna, Ironwood tree, Siamese senna
Flowering Period : October - March
Distribution : Native of South East Asia; now widely cultivated
Habitat : Planted as ornamental tree
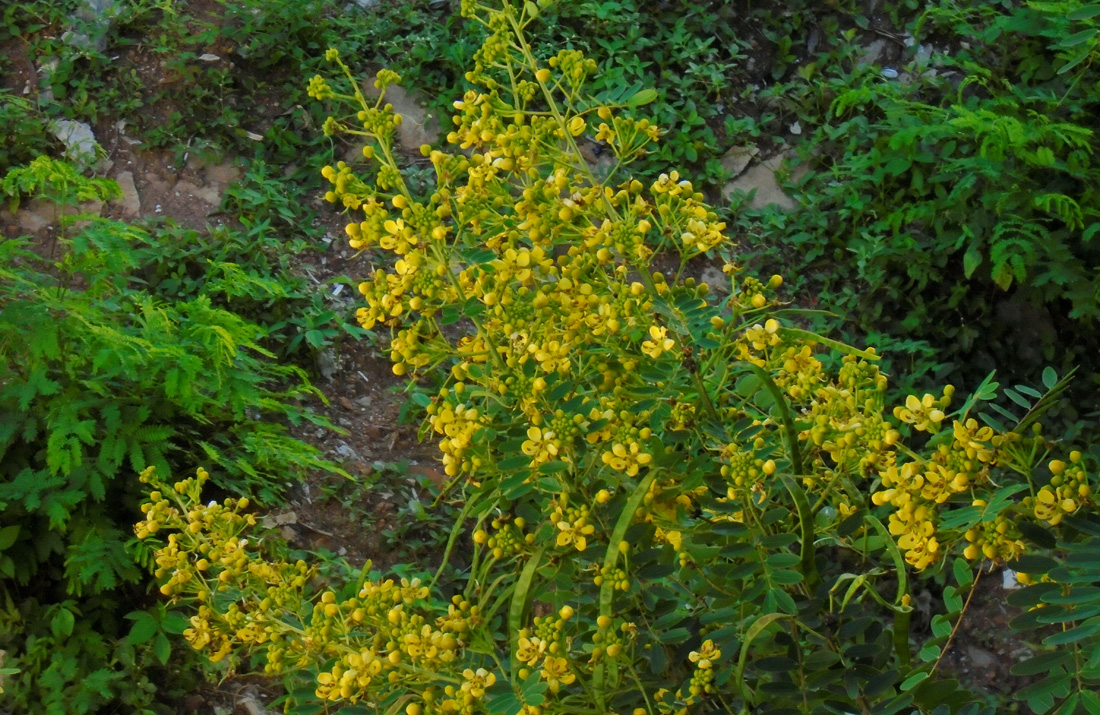

Uses : The young fruits and leaves are eaten as a vegetable. During preparation the cooking liquid is replaced 3 times to remove toxins. In traditional medicine, the fruit is used to charm away intestinal worms and to prevent convulsions in children. The heartwood is said to be a laxative, and a decoction is used against scabies. The tree is grown to provide shade along roads and in cocoa, coffee and tea plantations. It is also planted as a dense windbreak and shelterbelt. All parts of the plant can be used for tanning. The wood has also been used for poles, posts, bridges, mine poles and beams. Its charcoal is also of excellent quality.
Key Characters : Trees, to 12 m high; young parts puberulent. Leaves paripinnate,
alternate; stipules small, subulate, cauducous; rachis 30-35 cm long, slender,
pubescent, grooved above, pulvinate; leaflets 18-30, opposite; lamina oblong, elliptic-oblong or ovate-oblong.
Flowers bisexual, yellow, in terminal or axillary corymbose recemose panicles;
bracts linear, curved; sepals 5, suborbicular, subequal, greenish-yellow,
puberulent; petals 5, ovate-elliptic, subequal, clawed; stamens 10,upper 3
staminodes small, antheriferous ones 7, lower2 large, curved, one medium; ovary
half inferior, sessile, pubescent, deeply grooved, ovules many. Fruit a pod.


 Home
Home