Moringa
oleifera Lam. Gaertn.
മുരിങ്ങ
Family : Moringaceae
Synonym : Moringa oleifera Bedd.
Common Names : Muringa, Drumstick tree, Ben oil tree
Flowering Period : November – March
Distribution : Cultivated throughout India and many tropical countries
Habitat : Cultivated

Uses : The young leaves are taken internally to increase the milk flow in nursing mothers. The root juice is used internally in the treatment of asthma, gout, rheumatism, enlarged spleen and liver, bladder and kidney stones, inflammatory conditions. Externally, the root is used to treat boils, ulcers, glandular swellings, infected wounds, skin diseases, dental infections, snake bites and gout. The bark is an appetizer and digestive. The oil obtained from the mature seed and pods, known as 'oil of ben', has been used to lubricate watches and other fine machinery. The powdered seeds are used to clarify sugar cane juice. When the tree is injured, the stem exudes a gum that is used in calico printing.
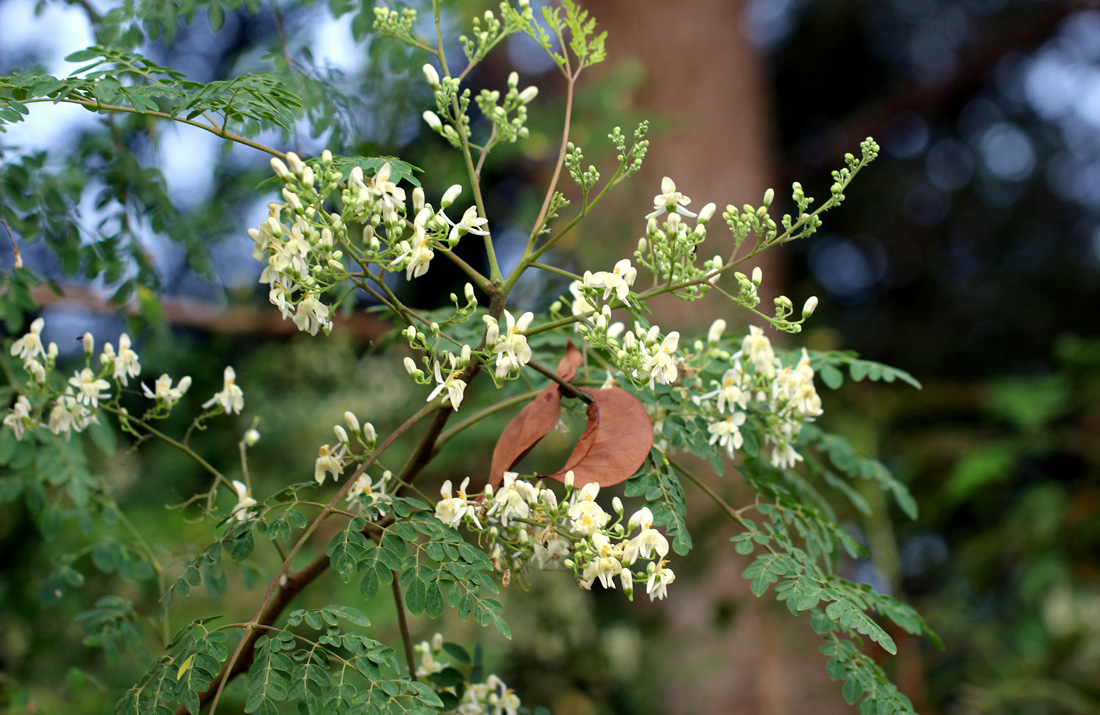
Key Characters : Small trees;
branchlets lenticellate. Leaves tri-pinnate, pinnae and pinnules opposite;
leaflets oblong, obtuse at apex, pubescent. Panicles axillary, tomentose;
flowers white; calyx lobes oblong, reflexed; petals spathulate, unequal;
fertile stamens 5; anthers one celled, intervened by 5 or 7 staminodes; ovary
1-celled, 3-valved, ovoid. Pod 9-ribbed;
seeds winged.


 Home
Home