Guazuma ulmifolia Lam.
കപട രുദ്രാക്ഷം
Family : Sterculiaceae
Synonym : Theobroma guazuma L
Common Names : Kapada rudraksham, Honey fruit tree, Bastard Cedar
Flowering Period : February – September
Distribution : Native of Tropical America
Habitat : Grown as avenue tree

Uses : The bark is the part most used. It is used as to induce perspiration, as a tonic and a blood cleanser and is employed to treat a wide range of disorders including; digestive tract problems such as gastrointestinal pain, liver problems, diarrhoea and dysentery; urinary and reproductive tract problems. The fruit (in Mauritius), the roasted seeds (in Java), and the bark (in India) are officinal remedies against elephantiasis. A natural pioneer species that colonizes recently disturbed areas; it is fast-growing, tolerant of full sunlight and provides food for the native fauna. It can be used as a pioneer species when restoring native woodland, but is best not used outside of its native range.
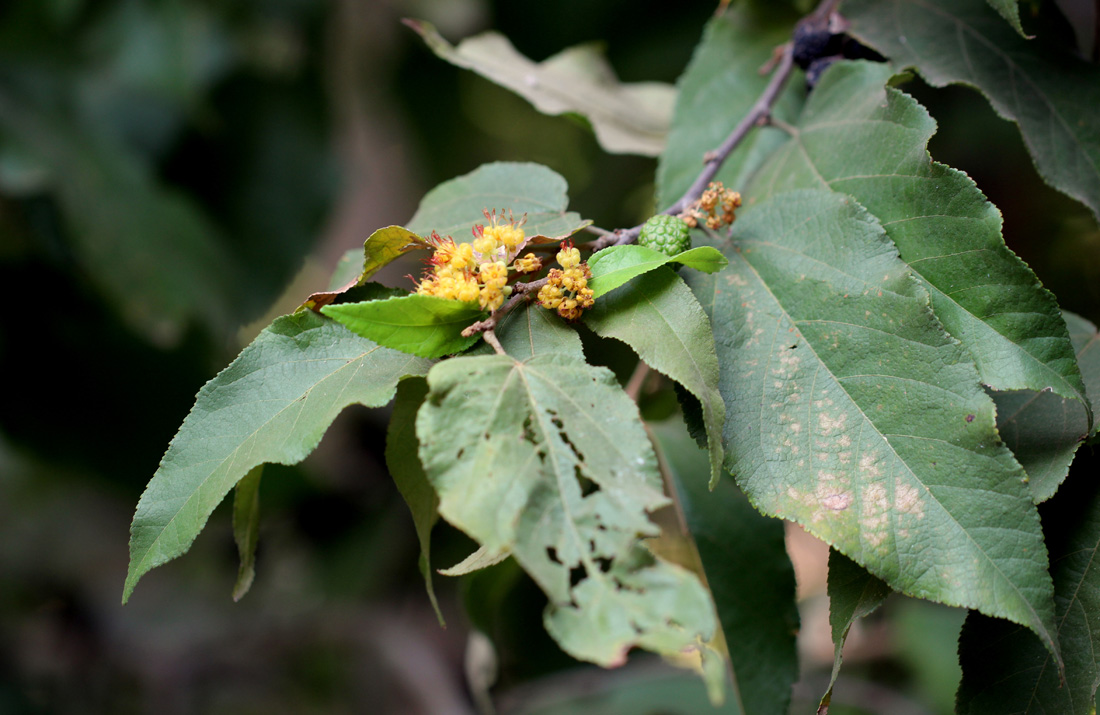
Key Characters : Guazuma ulmifolia are small or medium sized trees.
Leaves lanceolate, oblong-lanceolate or ovate, obliquely cordate at base,
serrulate at margin, acuminate at apex,
stellate-pubescent on both surfaces. Cymes axillary and terminal. Sepals
3-5, connate, elliptic-lanceolate or ovate, subequal, tomentose outside. Petals
obovate, concave with 2 apical appendages. Staminodes are petaloid. Ovary
globose, stellate-tomentose. Capsules subglobose, woody, tubercled.


 Home
Home