Diospyros
malabarica (Desr.) Kostel.
പനച്ചി
Family : Ebenaceae
Synonym : Diospyros peregrina (Gaertn.) Gurke
Common Names : Panachi, Vananji, Malabar ebony, Indian persimmon
Flowering Period : March – May
Distribution : Indo-Malaysia
Habitat : Evergreen forests and sacred groves
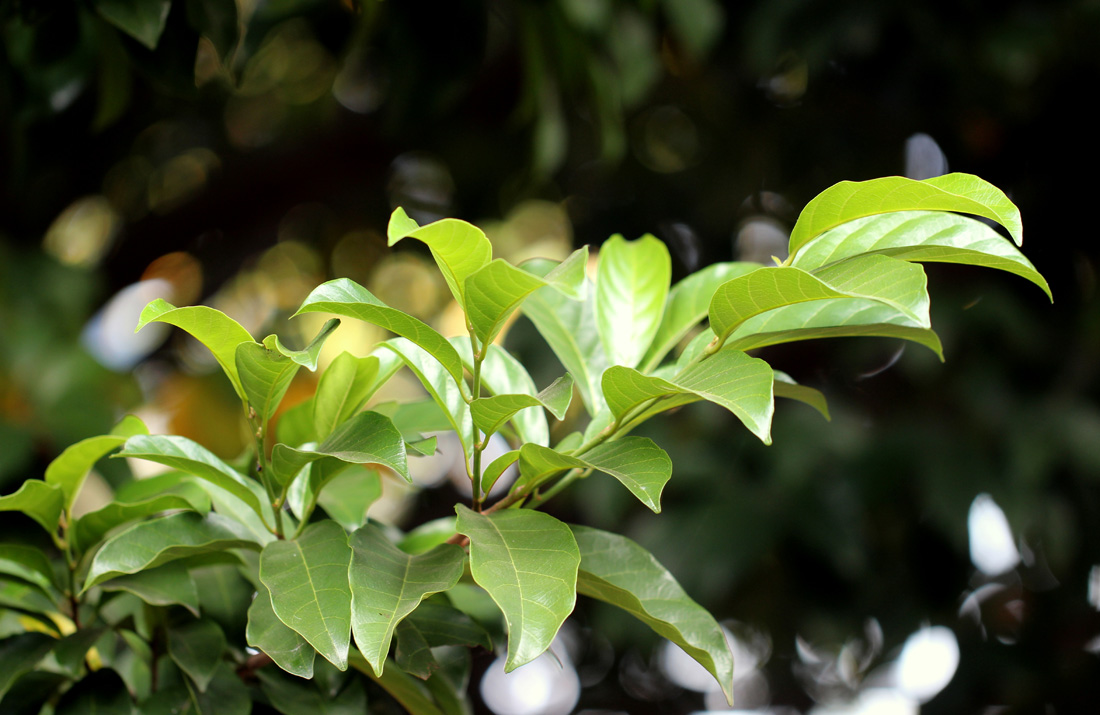

Uses : The fruit, when unripe, is said to be cold, light, and astringent; and to possess anti-bacterial and antihelmintic activity. The juice of the fresh bark is useful in the treatment of bilious fevers. Externally, the bark is said to be a good application for treating boils and tumors. The seeds are used as a treatment for diarrhoea and chronic dysentery. A dark oil prepared from the fruit makes an excellent varnish for paper umbrellas and fans. A valuable and highly decorative hardwood that is strong, hard, dense and very durable. It is used for items such as luxury furniture and wood carvings, and also as a raw material for boats and constructions.
Key Characters : Dioecious trees,
bark black with greenish tinge flaking off in thick scales. Leaves simple,
alternate, distichous; lamina oblong, margin entire. Flowers unisexual, pale
yellow; male flowers: 2-7 in axillary, drooping cymes; calyx lobes 4; corolla
campanulate; lobes 4, imbricate; stamens usually 40, in pairs; female flowers:
usually solitary, axillary, drooping; calyx deeply divided, lobes 4; corolla
campanulate, deeply divided, lobes 4; ovary superior, globose, 8-celled, ovule
1-in each cell. Fruit a berry.


 Home
Home