Bridelia retusa (L.) A. Juss.
മുള്ളുവേങ്ങ
Family : Euphorbiaceae
Synonym : Clutia retusa L.
Common Names : Mulluvenga, Asuvamaram, Kaini, Kadukumaram, Komanji, Mukkayini, Spinous kino tree
Flowering Period : August – December
Distribution : Indo-Malaya
Habitat : Semi-evergreen and deciduous forests, also in the plains

Uses : Ayurvedic, drought tolerant. The plant is pungent, bitter, heating, useful in lumbago, hemiplegia; bark is good for the removal of urinary concretions (Ayurveda). Root and bark are valuable astringents. The bark is used as a liniment with gingelly oil in rheumatism. The ripe fruit is edible.
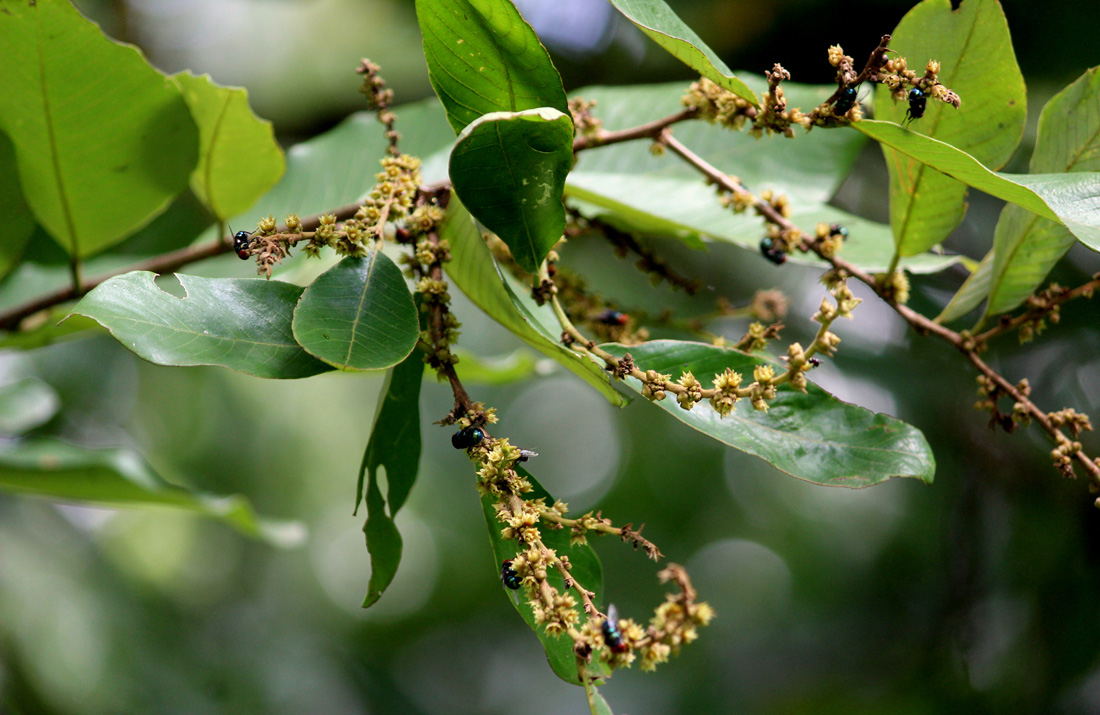
Key Characters : Briedelia retusa are deciduous trees bark
greyish-brown; young trees armed with sharp thorns. Leaves simple, alternate,
broadly elliptic, oblong, base round, margin entire, bright green and glabrous.
Flowers unisexual; greenish-yellow, sessile, crowded in dense axillary or
terminal. Male flowers: tepals 10, biseriate, valvate; stamens 5, monadelphous,
anthers oblong; pistillode bifurcate; disc annular. Female flowers: tepals 10,
biseriate, lanceolate, valvate; ovary
half inferior, globose, 2-locular, ovules 2 in each cell; styles 2. Fruit a
drupe, purplish-black.


 Home
Home